As Canadians, we often take pride in our nation's agricultural prowess, boasting high-quality products and sustainable farming practices. However, unnoticed in this success lies a pressing issue that threatens to undermine our agricultural sector's stability: the impending phosphate fertilizer crisis.
Phosphate fertilizer is a vital component for agricultural production, which is a major driver of Canada’s economy. Remarkably, Canada imports 100 per cent of the 2 million tonnes of phosphate fertilizer it requires, with the majority sourced from the United States. Canada’s reliance on imports leaves our agricultural production vulnerable to price fluctuations and supply instability. These realities pose significant risks that demand our immediate attention.
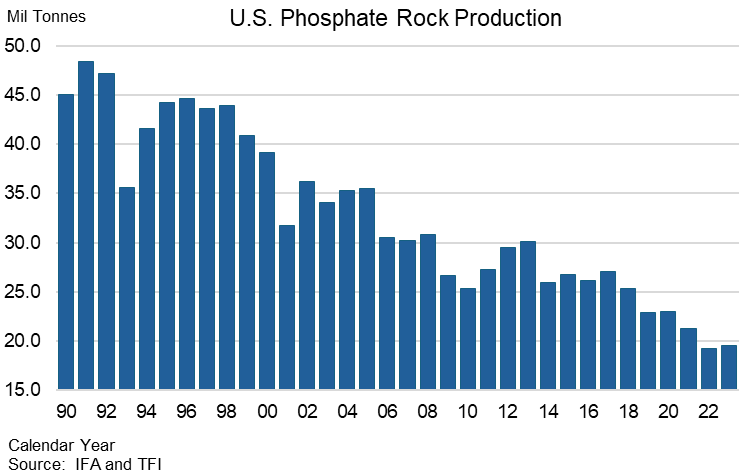
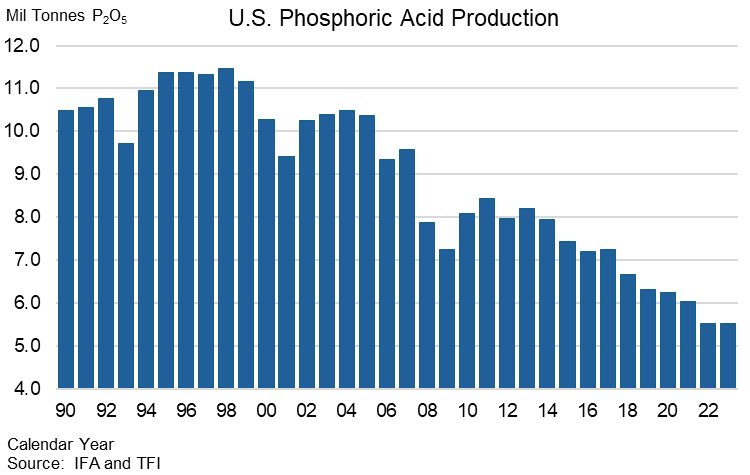
1. Growing Demand, Declining Supply: The demand for phosphate fertilizer is steadily increasing, while production in the United States is on the decline. With the possibility of Nutrien’s White Springs 500,000 tonne P2O5 phosphoric acid facility in northern Florida closing later this decade or early next due to a lack of phosphate reserves, this issue will be further exacerbated. This impending supply shock should serve as a wake-up call for Canadian policymakers and farmers.


2. New Demand: While Canada will continue to require more phosphate fertilizer for its expanding food crops, the development of Canada’s renewable diesel industry will also demand more oil seed production and thus greater phosphate fertilizer demand. Furthermore, Canadian farmers are now competing for the same supply of phosphate with the Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) battery market for electric vehicles and battery storage.
3. Geopolitical Vulnerability: With US supplies on the decline, Canada could be forced to rely on imports from non-allied countries like China and Russia who control 45 per cent of the global production of phosphate fertilizers, leaving us vulnerable to geopolitical tensions and export restrictions. Recent events, such as the Russia-Ukraine war and instability in the Middle East, have already disrupted supply chains, highlighting the urgency of securing a domestic supply.
4. Environmental Implications: Many phosphate fertilizers imported from the US are derived from sedimentary phosphate deposits and contain high levels of cadmium, a toxic heavy metal and carcinogen posing significant risks to soil health and food safety. The European Union has taken a leadership role in regulating cadmium levels, progressively lowering the maximum allowable levels of cadmium in the phosphate fertilizers it uses and updating the limits of cadmium permitted in its food supply.
In the past, Canada has responded to lower allowable levels of cadmium in wheat exports by employing selective breeding to reduce cadmium uptake. A more sustainable solution would be to reduce the direct application of cadmium to the soil. Using low cadmium phosphate fertilizers presents a more logical and responsible alternative to lowering cadmium levels in all cereals, pulses, and oilseeds.
Developing a domestic supply of phosphate from Canadian igneous deposits offers access to low-cadmium fertilizer options, while also aligning us with international fertilizer and food safety standards and promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
5. The Martison Phosphate Project: Fortunately, there is hope on the horizon. The Martison Phosphate Project, spearheaded by Fox River Resources, presents a promising solution to Canada's phosphate dilemma. Located in Ontario, this project boasts the highest-grade, cleanest undeveloped phosphate deposit in North America, with the potential to supply both Canada and the United States with phosphate products very low in cadmium and without geopolitical risk.
Recognizing these challenges, on June 10, 2024, the Government of Canada added phosphate to its Critical Minerals List.
The Government of Canada has made significant investments to support the development of critical mineral projects and associated value chains. These investments include the $1.5 billion Strategic Innovation Fund, the $1.5 billion Critical Minerals Infrastructure Fund, the Indigenous Natural Resources Partnerships Program, and Indigenous grants related to critical minerals infrastructure.
Now that phosphate has been added to Canada’s 2024 Critical Minerals List, projects like Martison can apply for federal funding under these programs and may also qualify for additional funding, incentives and supports from:
The Canada Growth Fund; The Business Development Bank of Canada; Export Development Canada; The Canada Infrastructure Bank; Sustainable Development Technology Canada; and, Scientific Research and Experimental Development tax incentives. Additionally, the federal government is working to streamline the permitting process for the development of critical mineral projects.Canada is working on a new Sustainable Agriculture Strategy which is expected to include soil health as an area of focus. Canada’s federal and provincial governments should consider adopting the EU's approach to managing cadmium in phosphate fertilizer products, with the aim of improved soil health and lower cadmium in our agri-food products.
Government policies must encourage development of Canadian phosphate resources, resources that fit with a sustainable agriculture policy that does not continue to add a carcinogen to our Canadian soils. Streamlining permitting processes, providing infrastructure funding, and offering financial incentives are just a few ways government can accelerate progress and mitigate the risks posed by the impending phosphate crisis.
As Canadians, we have a responsibility to safeguard our agricultural sector and protect the future of farming in our country. Developing a fully integrated phosphate facility takes many years, the time to act is now. Let us come together to address the looming phosphate crisis, develop a domestic supply of phosphate fertilizer, and secure a bright future for Canadian agriculture.
Fox River Resources is investing in the future of phosphate in Canada by developing the Martison Phosphate Project. Shares of Fox River Resources trade on the Canadian Stock Exchange under the ticker FOX.
Please click here to sign up and receive news from Fox River Resources. You can also email us at: info (at) fox-river.ca or call 416-972-9222 to speak with us directly.